If you are working in influencer marketing, you must have heard of the new buzzword: AI influencers.
AI influencers, also known as virtual influencers, are quickly becoming one of the most talked-about trends in the influencer marketing world. These digital personalities, often powered by AI and CGI, can look and behave like real people. Some are animated or stylized, while others are nearly indistinguishable from humans.
While AI influencers won’t replace human creators, they are changing the game, offering new opportunities for creative campaigns, brand storytelling, and customer interaction. Understanding how to work with these digital personas is key for marketers who want to stay ahead of the curve.
In this article, we explore the evolution of AI influencers, why they’re gaining popularity, how leading brands are using them, and what this trend means for the future of influencer marketing.
What Are AI Influencers?
AI influencers are digital personas created using AI tools and CGI. They behave like human influencers, posting content, engaging with followers, and partnering with brands, but they are not real people. Some are managed by agencies, while others are entirely autonomous with AI-generated visuals and personalities.
According to The Conversations, there are three main types of AI influencers:
- Non-Humans – Characters that are clearly fictional (e.g., mascots).
- Animated Humans – Stylized or cartoon-like personas.
- Hyper-Realistic CGI Humans – Nearly indistinguishable from real people.
Some of the most well-known examples include:
- LilMiquela – Fashion and music influencer with over 2.7M followers.
- Imma – A Japanese virtual model with a highly engaged following.
- Kuki – An interactive chatbot with a social media presence.
A Brief History of Virtual Influencers
The concept of AI influencers first came out can be traced back to the early 2010s.
Back in those days, the early version of AI influencers were simply virtual characters in the gaming and entertainment industry.
As AI and computer graphics developed, these characters started to have more nuances and became more sophisticated, eventually becoming the virtual influencers we see today.
In 2016, the world welcomed Lil Miquela who is considered the first official hyperrealistic AI influencer in history. After her release, there were a ton of debates about whether she was a real person or not.
Since then, the virtual influencer industry has exploded:
- CB from Casa Bahia – A Brazilian virtual mascot with over 10M followers.
- Milla Sofia – An AI-generated influencer using diffusion models.
- Brand-created influencers – From Lu of Magalu to Noonoouri, companies are building and managing their own digital ambassadors.
Why Are Brands Turning to AI Influencers?
Though still niche, AI influencers appeal to brands for several compelling reasons:
- Total control over content, messaging, and brand representation
- No scandals or PR risks, unlike human influencers
- Always available for campaigns and engagement
- Cost-effective over time
- High novelty value, boosting brand buzz and attention
Besides those reasons, according to Influencer Marketing Hub data, AI influencers are collecting excellent feedback from the marketers who worked with them and inspiring more collaborations:
- 59.8% of marketing professionals have worked with AI influencers
- 15.5% plan to collaborate with AI influencers
- Over 60% of those who once collaborated with virtual influencers are satisfied.
Since AI influencers don’t exist as people outside of their social media feed, there is a team of professionals managing them, it is easier to have them align with the specifics of a marketing campaign.

Case Studies: How Brands Are Using AI Influencers
Although there is still no data about how effective AI influencers are compared to traditional influencers is clear the fit with the product is still the most critical factor for a successful influencer marketing campaign.
Audiences might be happy to see the innovation of AI influencers, but they may find human influencers more relatable regarding certain products.
Still, AI influencers are great if brands want to showcase an innovative image and position themselves at the forefront of a trend.
We’ve found 3 case studies in different industries to help you get to know better how to work with AI influencers.
1. Hugo Boss Rebranding: Rebranding With Imma & Nobody Sausage
In the spring of 2022, the German fashion brand Hugo Boss underwent a major rebranding effort to reach the younger generations. First of all, it was the campaign, which included many traditional fashion influencers such as Kendall Jenner and Hailey Bieber.
In addition, they partnered with Nobody Sausage and Imma, two of the most well-known AI influencers in this field.
It was a powerful signal to integrate virtual influencers in the rebranding, which showed that Hugo Boss’s future will focus on technology and innovation.
2. Samsung x Miquela: A Digital-First Dream
Miquela Sousa, created by Brud, partnered with Samsung as part of its #TeamGalaxy campaign. The collaboration highlighted the futuristic appeal of both the Galaxy smartphone and its ambassador. The campaign effectively reached tech-savvy digital natives and reinforced Samsung’s innovation narrative.
3. Dior x Noonoouri: A Virtual Icon for a Classic Brand
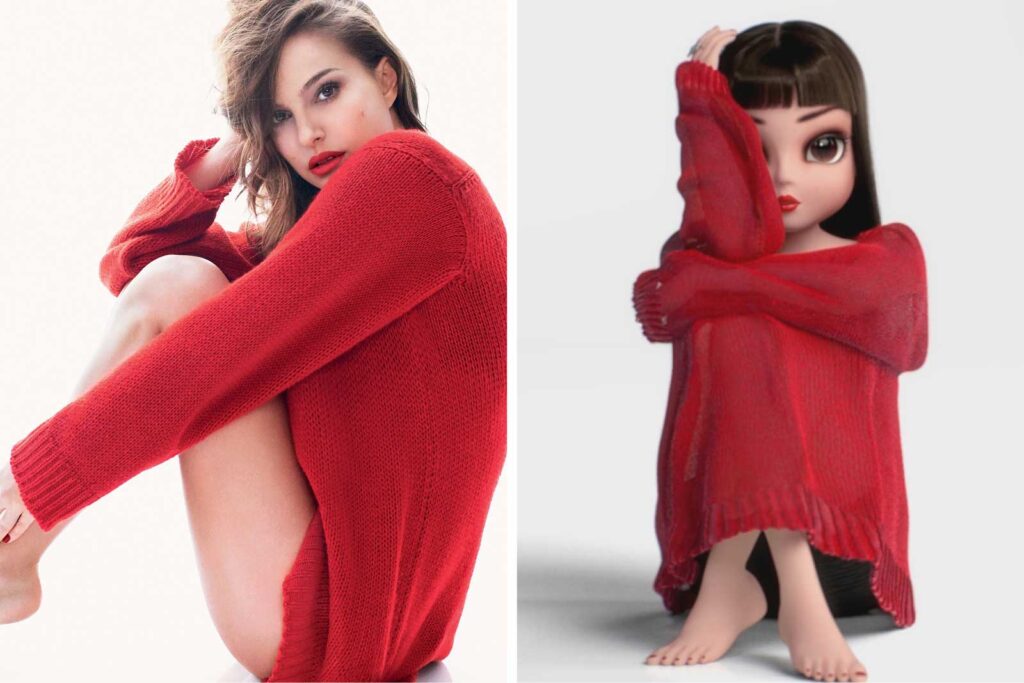
In 2018, luxury meets digital with Noonoouri’s campaign for Dior’s “Rouge” perfume. In a side-by-side recreation of Natalie Portman’s classic ad, Noonoouri added novelty and visual intrigue. This AI-led approach helped Dior appeal to both fashion lovers and early adopters of virtual media.

4. Magalu’s Lu: A Virtual Face of Retail
Lu of Magalu is not just a virtual influencer. She is the face of the leading Brazilian retail chain Magalu. Her profile blends memes, reels, relatable content, promotions, and branded content. By developing its influencer, Magalu can provide a more interesting face to its promotion and resonate better with the clients.
5. Coach x Imma: Storytelling That Blends Real & Virtual
Coach’s 2024 “Find Your Courage” campaign merged CGI and real personalities. Imma’s story—her journey to become human—ran alongside stars like Lil Nas X and Camila Mendes, showcasing how virtual influencers can amplify emotion-driven narratives through immersive storytelling.
What’s Next: The Future of AI Influencers
With tools like Midjourney, ChatGPT, and Runway advancing rapidly, brands and creators alike are experimenting with AI-powered personas that can communicate, adapt, and even develop unique personalities over time. Whether it’s for cost-efficiency, creative flexibility, or 24/7 availability, AI influencers are unlocking new ways to build audience engagement and brand value.
AI Influencers for Brands
Many established AI influencers are created by marketing agencies at high costs. However, with the rise of ChatGPT, specialized LLMs, and GAN models, brands can now easily generate AI influencers tailored to their image and goals.
Tools like SynthLife enable the creation of realistic characters with branded elements, extending beyond images to AI-generated videos. Combined with AI-powered chatbots, these influencers offer 24/7 personalized social media engagement, acting as powerful brand advocates.
Why AI Influencers Work for Brands
Customers seek intimate, personalized interactions with brands, not just one-way messaging. Brands can meet this demand either by expanding costly support teams or by deploying AI influencers and chatbots that deliver personalized attention efficiently.
Effective AI influencers boost customer engagement, increasing social media following, visibility, and conversions by providing constant support and interaction.
The Future of AI and Branding
As AI influencer creation becomes simpler and largely self-sustaining, many brands will integrate AI characters into their core marketing strategies. These influencers offer a humanized yet curated brand presence, fulfilling consumers’ desire for thoughtful, authentic interaction.
Legacy brand characters brought to life as AI influencers will also capture significant attention, opening a new dynamic channel for brand storytelling and engagement.
AI Influencers for Content Creators
AI influencers will significantly impact content creators—not by replacing them, but by enabling virtual clones that offer fans a more intimate, personalized experience.
For example, Caryn Marjorie pioneered this with Caryn AI, created in partnership with Forever Voices AI. Her AI clone, trained on hundreds of thousands of interactions, allows fans to chat directly with a virtual version of her. This innovation earned $72K in its first week and is projected to generate $5 million monthly as her following grows.
The Future of AI for Content Creators
Like brands, content creators will increasingly use AI tools and clones to deepen audience connections. Creators’ unique personalities, which build strong parasocial bonds, can be replicated by AI for personalized 1-to-1 interactions, boosting monetization and engagement.
Creators known for niche expertise can also train AI on their vast content libraries, offering fans faster, more intuitive access to their knowledge.
Overall, AI will drive a surge of innovative applications among content creators, transforming how they connect with and serve their audiences.
Final Thoughts
AI influencers are not just a passing trend, they’re the next evolution of digital branding and content strategy. For both brands and creators, the ability to scale engagement, personalize experiences, and control messaging offers significant long-term value.
As technology matures, expect AI influencers to become more intelligent, expressive, and seamlessly integrated into the digital experience.
FAQs about Virtual Influencers
1. How do AI influencers maintain engagement and authenticity in interactions with their followers, given their non-human nature?
AI influencers engage followers through programmed responses and content that resonates with audience interests, though this might lack the depth of human interaction.
2. What ethical considerations might arise in using AI influencers, especially concerning transparency and disclosure to audiences?
Ethical concerns include the need for transparency about their AI nature to avoid misleading audiences.
3. How is the content creation process involving AI influencers managed, and who is responsible for it?
The creative process involves teams of designers and AI specialists who develop the influencer’s persona and content, ensuring alignment with brand and audience expectations.


![Influencer Video Marketing That Works [Guide]](https://www.creatordb.app/wp-content/uploads/ChatGPT-Image-Jun-13-2025-03_32_35-PM.png)

